Weight-loss surgery is proven to have a positive impact on fertility for individuals struggling with obesity. Excess weight can have a significant effect on reproductive health and increase the risk of infertility. (1)
If you’ve been trying to conceive without success and are considering weight reduction interventions, Dr. Ricardo Bonnor, MD, FACS, FASMBS at Texas Endosurgery Associates in Houston is here to help.
Explore how weight-loss surgery can boost your fertility by contacting Texas Endosurgery Associates today. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Bonnor by calling (281) 579-5638.
Contents
How Can Obesity Affect Fertility?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body weight and high body mass index (BMI). Beyond the well-known associated health risks, such as diabetes and heart disease, recent research suggests that being overweight may also have a significant impact on reproductive health, particularly in regard to fertility.
Excess weight can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and reduced ovulation. (2) Additionally, it can affect the quality of eggs and sperm, making it more challenging to achieve pregnancy. Weight-loss surgery addresses these issues by promoting weight management and improving overall health.
Dr. Bonnor offers a comprehensive approach to fertility enhancement through bariatric surgery, focusing not only on weight loss but also on improving metabolic function and reproductive health.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that can have a significant impact on fertility. Studies show that between 40%-80% of women with PCOS are overweight or obese. (3) This hormonal disorder affects the reproductive system and is characterized by hormone imbalances, specifically elevated levels of androgens (male hormones), which can disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries.
One of the key factors that contribute to infertility in women with PCOS is insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, but in women with PCOS, the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can result in higher levels of insulin in the blood, which can stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens and disrupt the normal release of eggs. (4) Furthermore, the presence of ovarian cysts, another characteristic of PCOS, can also interfere with fertility. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries and can prevent the release of mature eggs during ovulation.
How Can Weight-Loss Surgery Help?
Research has shown that weight-loss surgery can lead to a higher rate of spontaneous ovulation and an increased likelihood of successful pregnancies. In fact, one study showed that after two and a half years, 69% of infertile obese women were able to conceive. (5) By addressing obesity and its associated hormonal imbalances, weight-loss surgery can provide a holistic approach to improving fertility outcomes.
Can Weight-Loss Surgery Help Everyone with Fertility Issues?
It’s important to note that weight-loss surgery is not a guaranteed solution for infertility, and individual results may vary. However, for individuals struggling with obesity and infertility, weight-loss surgery offers a potential pathway toward enhancing reproductive health and increasing the chances of conceiving.
Benefits of Boosting Fertility with Weight-Loss Surgery
- By reducing obesity, individuals can increase their chances of conceiving and starting a family.
- Addressing hormonal imbalances paves the way for improved fertility in both men and women.
- Weight loss has been shown to restore regular menstrual cycles, enhancing the likelihood of successful ovulation.
- Losing weight can lead to significant improvements in sperm motility and production.
- Weight loss has been shown to help manage PCOS symptoms, restore hormonal balance, and improve fertility outcomes. (6)
- With weight-loss surgery, patients can achieve better possible responses to fertility treatments such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF).
- By adopting a healthy lifestyle and shedding excess weight, individuals can experience improved overall health, leading to a better quality of life for themselves and their future family.
Weight-Loss Surgery for Boosted Fertility
Sleeve Surgery
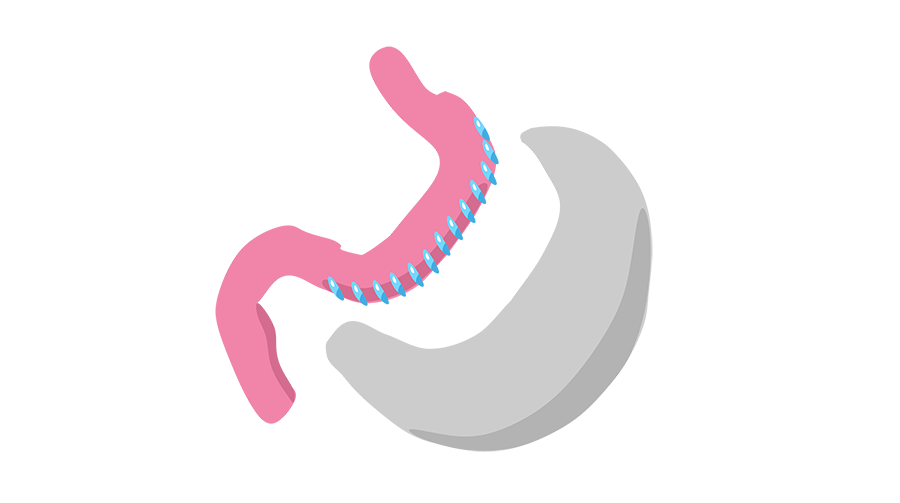
Sleeve surgery, gastric sleeve, or vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) is a minimally invasive surgical technique that involves the removal of a large portion of the stomach, resulting in the creation of a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach pouch. A report by the International Summit of Sleeve Gastrectomy found that participants lost a mean average of 62.7% of excess weight after a year, and 60% of their excess weight after 5 years. (7) By undergoing sleeve surgery, individuals may experience substantial weight loss, leading to improvements in their overall health and reproductive function.
Gastric Bypass
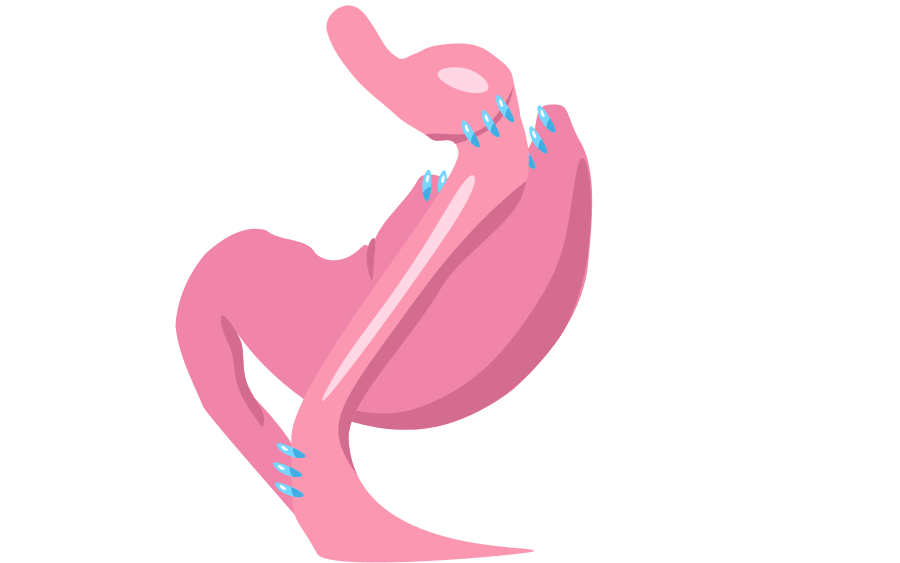
A gastric bypass creates a small stomach pouch while rerouting the gastrointestinal tract past the vast majority of the stomach and duodenum (the first section of the small intestine), then reconnecting it with a lower part of the system. The most common technique used is the Roux-en-Y method. During the procedure, the stomach is divided into a smaller upper pouch and a larger lower pouch. The upper pouch is then connected directly to the small intestine in a Y-shaped configuration. This creates a new pathway for food to bypass a portion of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine. Gastric bypass surgery can address fertility concerns by promoting substantial weight loss and improving metabolic functioning.
Revision Lap Band

Also known as a gastric band revision, lap band revision is a surgical procedure performed to modify or adjust a previously placed adjustable gastric band. The adjustable gastric band, often referred to as a lap band, is a device that is placed around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch. This pouch restricts the amount of food that can be consumed, leading to feelings of fullness and promoting weight loss. However, in some cases, patients may experience complications or inadequate weight loss results with their initial lap band surgery, necessitating a revision procedure.
Revision Sleeve
There are several reasons why a patient may choose to undergo gastric sleeve revision. One common reason is inadequate weight loss. While the majority of patients experience successful weight loss after the initial gastric sleeve surgery, there are instances where individuals may not achieve their desired results. This can be due to various factors such as a larger-than-expected stomach pouch, stretching of the pouch over time, or insufficient restriction on food intake. In these cases, a revision gastric sleeve can involve resizing or reshaping the stomach pouch to enhance its restrictive capacity and promote further weight loss.
Duodenal Switch Surgery

A duodenal switch surgery involves two main components: restrictive and malabsorptive. The surgeon reduces the size of the stomach by creating a smaller sleeve-shaped pouch, limiting the amount of food that can be consumed at one time. This restrictive aspect helps individuals feel full more quickly and promotes portion control. The surgery also involves rerouting a portion of the small intestine. This malabsorptive component aims to reduce the absorption of calories and nutrients, which further enhances weight loss. The rerouting of the intestines allows food to bypass a significant portion of the small intestine, reducing the body’s ability to absorb calories and fat.
SADI: Single Anastomosis Duodenal Interposition

SADI, one anastomosis duodenal switch, or Loop DS is a variation of the duodenal switch procedure. Like the duodenal switch, it is both restrictive and malabsorptive. The two-part surgery starts with sleeve gastrectomy, creating a long vertical tube shape from the stomach. The surgeon then reroutes the small intestine in a way similar to the Roux-en-Y bypass, but in the shape of an omega.
How Much is Weight Loss Surgery in Houston?
As every patient’s treatment plan is different, Dr. Bonnor will provide information about the cost of your surgery after your personal consultation. For more information, or to book a one-on-one meeting at Texas Endosurgery Associates, call (281) 579-5638 or complete an online inquiry form.
Commonly Asked Questions (FAQ)
Will losing weight improve my fertility levels?
The benefits of bariatric surgery on fertility are multi-faceted. Weight loss achieved through bariatric surgery can restore hormonal balance, particularly in conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), where insulin resistance and high levels of androgens contribute to infertility. By reducing weight and improving insulin sensitivity, bariatric surgery can regulate menstrual cycles and increase the likelihood of ovulation.
Can weight-loss surgery help me conceive?
By undergoing bariatric surgery, patients can experience substantial weight loss, resulting in improved reproductive health. Studies have shown that weight loss surgery can lead to increased chances of conception, as well as higher success rates in assisted reproduction techniques.
Does weight affect sperm production?
Research has shown that excess weight can disrupt hormone levels in the body. This can lead to imbalances that negatively impact sperm production and function. Additionally, obesity is associated with increased inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which can damage sperm cells and impair their ability to fertilize an egg.
References
- Ozcan Dag Z, Dilbaz B. Impact of obesity on infertility in women. Journal of the Turkish German Gynecological Association. 2015;16(2):111-117. doi:https://doi.org/10.5152/jtgga.2015.15232
- Itriyeva K. The effects of obesity on the menstrual cycle. Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care. 2022;52(8):101241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cppeds.2022.101241
- Sam S. Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Obesity Management. 2007;3(2):69-73. doi:https://doi.org/10.1089/obe.2007.0019
- Fica S, Albu A, Constantin M, Dobri G. Insulin resistance and fertility in polycystic ovary syndrome. Journal of Medicine and Life. 2008;1(4):415-422. Accessed October 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3018970/#:~:text=In%20recent%20years%20it%20has
- Nori W, Akram W, Ali EA. Fertility outcomes following bariatric surgery. World Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2023;13(1):1-3. doi:https://doi.org/10.5493/wjem.v13.i1.1
- Kataoka J, Tassone E, Misso M, et al. Weight Management Interventions in Women with and without PCOS: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2017;9(9):996. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090996
- Hoyuela C. Five-year outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a primary procedure for morbid obesity: A prospective study. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery. 2017;9(4):109-117. doi:https://doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v9.i4.109









